Internally Flawless:
No inclusions, only blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.
Buying a diamond does not have to be an uncomfortable experience. The Diamsty Diamond Education Guide is designed to give you the tools and information you need to properly evaluate diamond quality and value with confidence.
Every diamond is unique, and there are a variety of factors which affect the price of a diamond. Focus on those factors most important to you, and choose a diamond that satisfies your individual standards for beauty and value. This might be a very different diamond than someone else with a similar budget would choose. At Diamsty, we want to help find the best diamond for you.
Every diamond certified by the GIA undergoes a thorough, independent evaluation. Here you will learn how GIA diamond grades are established, and how those grades affect the diamond’s price. Each of the four C’s (Carat Weight, Cut, Color, Clarity) is accompanied by a diamond chart illustrating the differences between grades.
After learning more, if you need to see diamonds in person, visit your local jewelry store. Get a better sense of what you personally value in a diamond. Note the color, cut, and clarity that best fit your needs. While you’re there, compare the prices with what you find at Diamsty. We’re confident you will be pleased with what you find.
Learn how diamond color is measured
How to read a diamond clarity chart
How diamond carat size affects price
How diamond cut affects appearance & beauty
See every round and
fancy diamond shape
Understand key terms and measurements
On the impartial grading of diamonds
Diamonds come in a variety of colors, some of them highly prized (pinks, blues, even yellow). However in a white diamond, the presence of a yellow tint will lower the price of a diamond. The less body color in a white diamond, the more true color it will reflect, and thus the greater its value.
Every Diamsty Diamond has been assigned a color grade by the GIA in a viewing environment specially designed to eliminate color from surrounding surfaces as well as the light source itself. This allows the color of the diamond to be accurately measured. Minor differences in diamond color detected in this environment are very difficult if not impossible to detect in a normal environment. The diamond industry has adopted the GIA diamond color scale; almost every diamond sold today is rated using the GIA color scale, whether it was actually certified by the GIA or not.
The photo below shows a master set used by gemologists to grade color in diamonds.

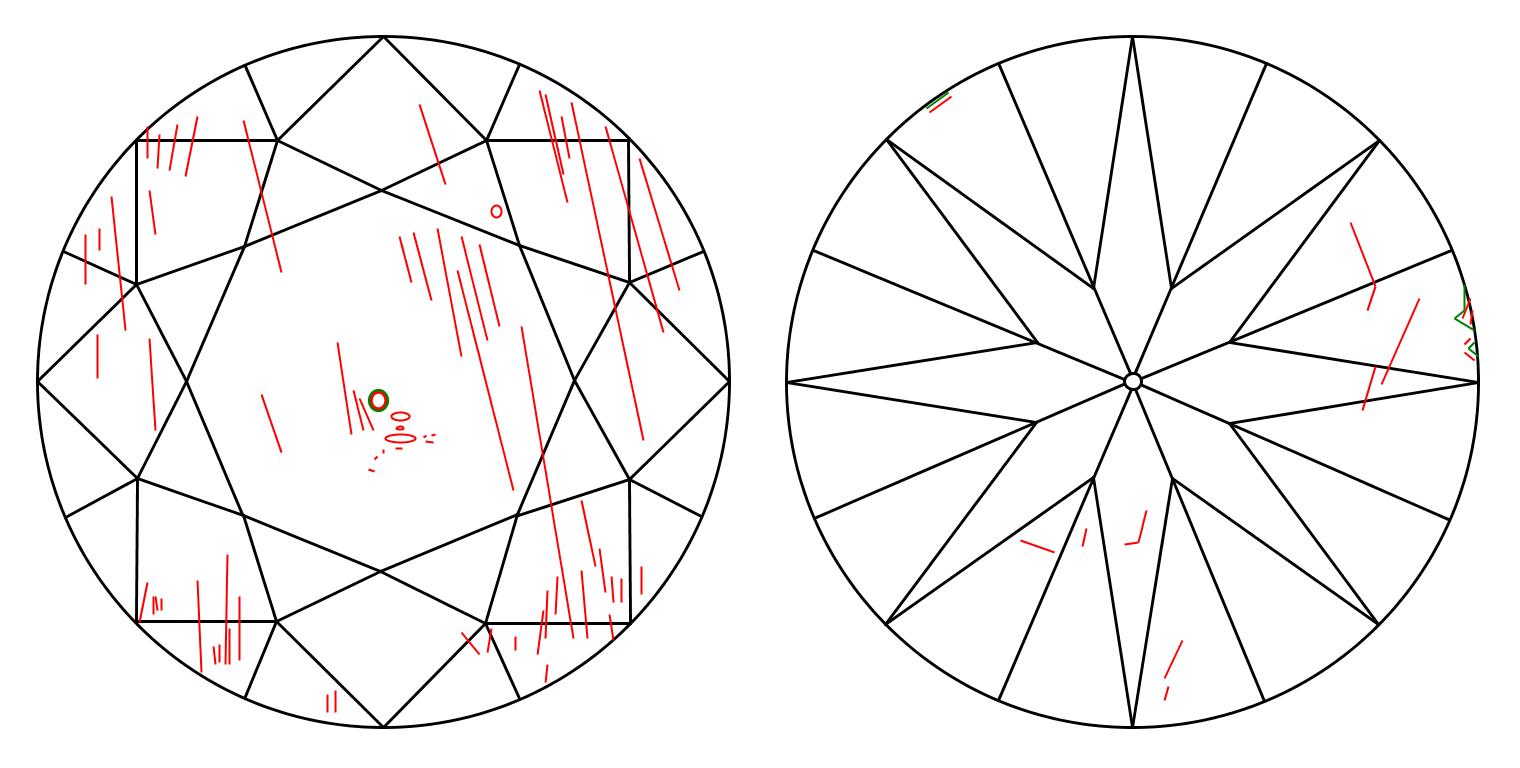
Because they are formed deep within the earth, under extreme heat and pressure; virtually all diamonds contain "birthmarks"; small imperfections inside the diamond (called inclusions), or on its surface (called blemishes). Clarity refers to the degree to which these imperfections are present. Diamonds which contain numerous or significant inclusions or blemishes have less brilliance because the flaws interfere with the path of light through the diamond.
The position of an inclusion affects how easily it can be seen. Diamond cutters make every effort to cut a stone so that inclusions are not visible through the table of the finished diamond. The preferred position for inclusions is under the bezel facets or near the girdle because they are harder to see there.
No inclusions or blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.
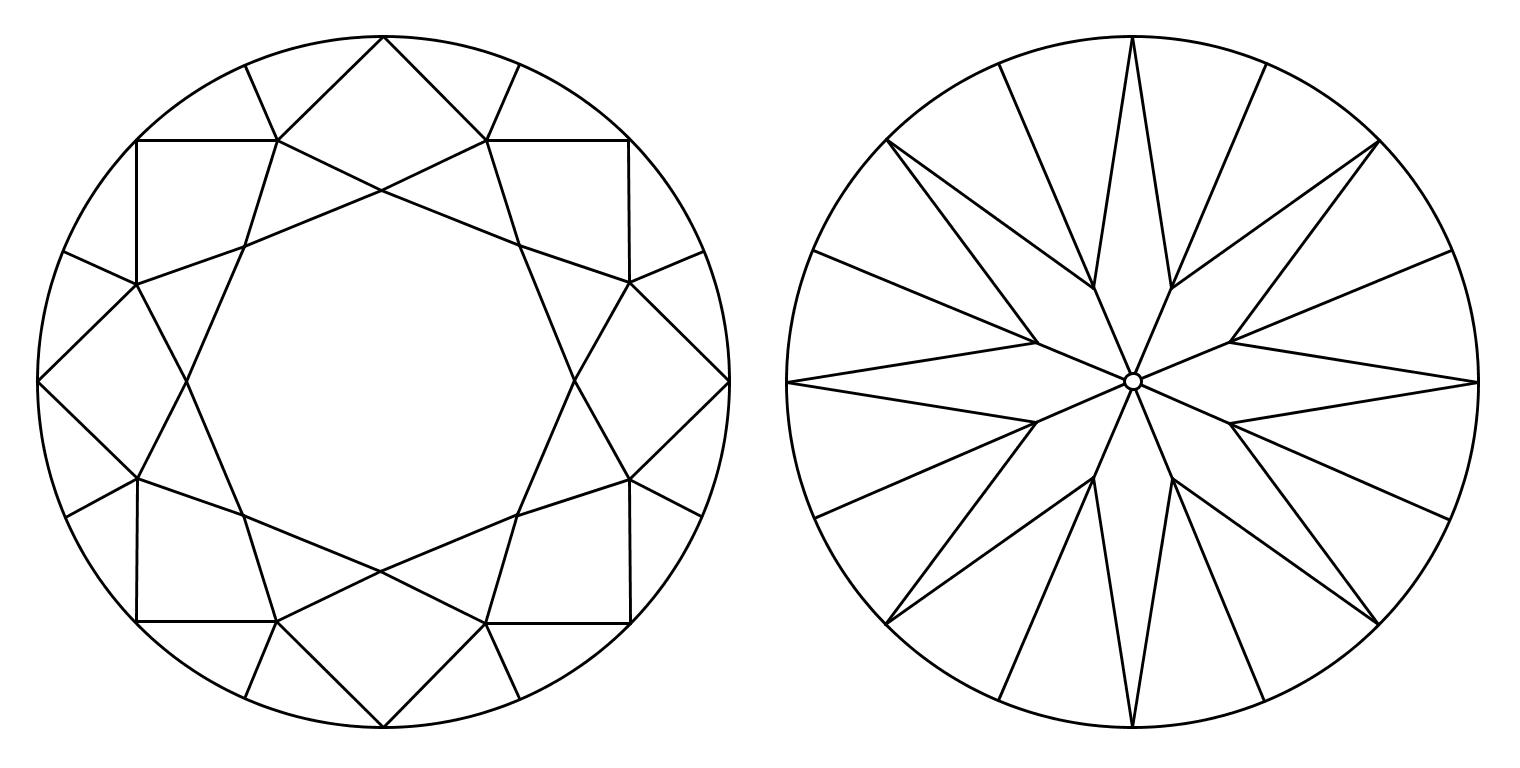
No inclusions, only blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.
Inclusions are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification.

Inclusions are clearly visible under 10x magnification but can be characterized as minor.

Inclusions are noticeable to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.

Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification and may affect transparency and brilliance.
The unique unit of weight measurement used to weigh diamonds. The term carat is derived from the Greek word kerátion which translates to carab seed. The carab seed was used by diamond traders as a unit of weight.
Caratage today refers to the weight of the diamond. A carat can be converted to 200 milligrams. Moreover, a carat can be further divided into 100 points to allow accurate measurements.
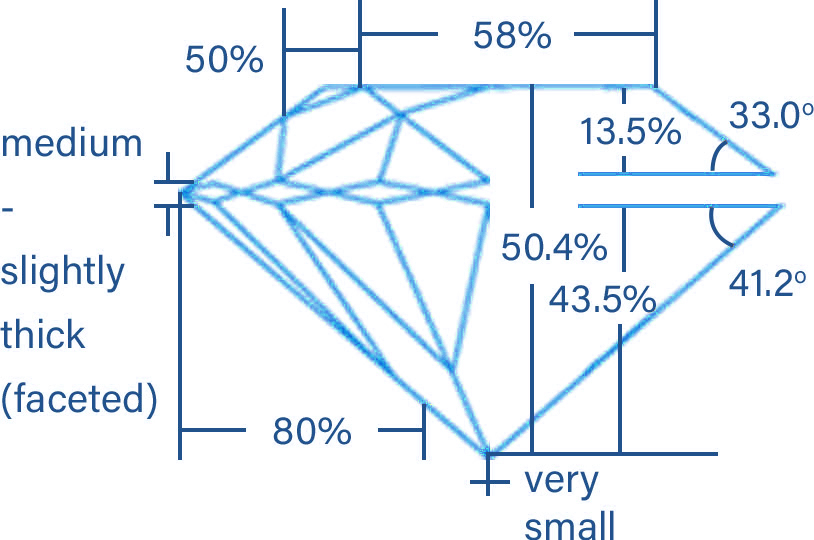
Determines Diamond's beauty, brilliance, fire & sparkle. A diamond's cut refers to its shape as well as its interaction with light i.e. how the diamond's facets reflect light, it depend on balance of proportion, symmetry & polish. An excellent cut diamond will have enhanced brilliance and make the diamond sparkle. GIA grades the cut of a diamond from excellent to poor.
Virtually all diamond cuts sold for use in jewelry are one of ten round or fancy diamond shapes. The most popular diamond shapes are:
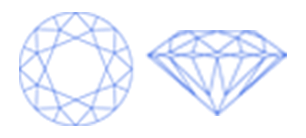
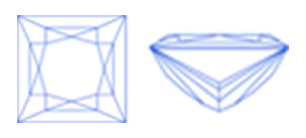

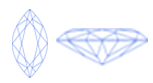


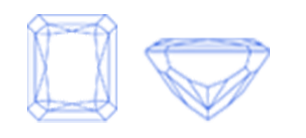



Once cut and polished, all diamonds possess a shared set of characteristics, often referred to as the anatomy of the diamond. While the individual proportions, angles and placement of these common characteristics vary for diamonds of different shapes, their definition is the same.
Before being purchased, many diamonds, and all Diamsty Diamonds (with the exception of our diamond stud earrings) are sent to a third party laboratory for a comprehensive evaluation; a process known as diamond certification. A reputable lab is one staffed by professional gemologists who specialize in diamond grading. Each diamond certificate issued is uniquely numbered, and corresponds to one individual diamond. From that point forward, the diamond and certificate (laminated to prevent tampering or damage) will travel together from seller to buyer.
Laboratory certification provides an impartial judgment of the characteristics and quality of each diamond. This certification (called a grading report, or dossier by GIA) gives the purchaser added confidence that the diamond received is as described by the seller. The diamond certificate is also valuable for insurance purposes, as it provides a professional, independent evaluation of the diamond.
A laboratory certification is not an appraisal. An appraisal seeks to establish the value of an item, mainly for insurance purposes. A diamond certificate does not evaluate a diamond's market value, only its characteristics and quality. That said, diamond certification from a reputable laboratory is invaluable in generating an accurate appraisal.